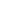
Some of the most common trade terms and their meanings:
| Term | Meaning | Information |
| LOI | Letter of Intent | Issued by Buyer. 1 page letter contains details of what Buyer wants. Item Amount? Where deliver to? Payment method? Specific requirements? |
| ICPO | Irrevocable Corporate Purchase Offer | More info than LOI. Would include bank details. |
| SCO | Soft Corporate Offer | From supplier. What they can supply, specs, and price. |
| FCO | Full Corporate Offer | Buyer requests an FCO from Buyer. This will include detailed specs and procedures for closing the deal. |
| SPA | Sales and Purchase Agreement (Contract) | The main contract. Details of every aspect of the transaction. |
| PI | Proforma Invoice | The amount that the buyer must pay. (Partial or full!). If partial, balance will be paid on BL/SGS. |
| BL | Bill of Lading | Product is loaded onto ship. |
| SGS | Name of inspection company | SGS inspects load and report sent to Buyer. |
| BCL | Bank Confirmation Letter | Buyer proves to Supplier that they have funds to continue. |
| POF | Proof of Funds | Buyer proves to Supplier that they have funds to continue. |
| POP | Proof of Product / Certificates | Supplier supplies proof of product to Buyer. |
| EXW | Exworks | Buyer wants to pick up product direct from Supplier business / warehouse. Supplier has no transportation / insurance costs. Buyer tasks on all transportation organizing / risks. |
| FOB FCA | Free on Board Free Carrier *Almost the same. Only difference: FOB = Non-Containerized Only FCA = Containerized and Non- Containerized. | Supplier responsible for: Getting goods to and loading onto ship. Export clearance Buyer responsible for everything else: Transport onwards. Bill of Lading fees Insurance Unloading fees, Transport from destination port to Buyer business. Example: FOB Tilbury UK. Port that the Supplier will deliver the goods to (and load onto ship). |
| CFR | Cost and Freight | Supplier responsible for costs up to the destination (unloading) port, includes: Export clearance, Bill of Lading Transport costs to unloading port. Note: CFR does not cover insurance. Buyer takes responsibility for any risks during transport and gets their own insurance. Example: CFR Southampton UK. |
| CIF CIP | Cost, Insurance & Freight Carriage and Insurance Paid *Almost the same. Only difference: CIF = Non-Containerized Only CIP = Containerized and Non- Containerized. | As CFR but Supplier takes responsibility for risk and covers insurance, up to destination (unloading) port. Note: Might find some suppliers that just use CIF term, even when its Containerized and Non-Containerized items! Just something to be aware of! Example: CIF – Koper, Slovenia Cost, Insurance and Freight to ‘Koper’, provided by supplier. |
| CPT | Carriage Paid To | Supplier is responsible for: Clearing the goods for export, Delivering them to the first carrier or another person stipulated by the Supplier at a named place of shipment (usually a foreign freight terminal) Then risk transfers to the buyer. |
| DAT | Delivered at Terminal (now called DAP, but old term might be used) | The supplier of a product delivers it to a previously specified terminal. Until then he has to shoulder the full costs and the risk of transport. |
| DAP | Delivered at Place (was DAT, both terms the same and might be used!) | Supplier delivers goods to the agreed place at destination. Supplier assumes all cost and risk until the goods are ready for unloading at named place at destination. |
| DDP | Delivery Duty Paid | The Supplier is responsible for organizing transport and paying duties and taxes. The exporter bears a higher risk. |
| FAS | Free Alongside Ship | FAS means the Supplier has fulfilled its obligation when the goods are placed alongside the ship. However, it is not recommended to use this rule if the buyer is not able to pay the costs related to the export of the goods. |